OpenELM: An Efficient Language Model Family with Open-source Training and Inference Framework
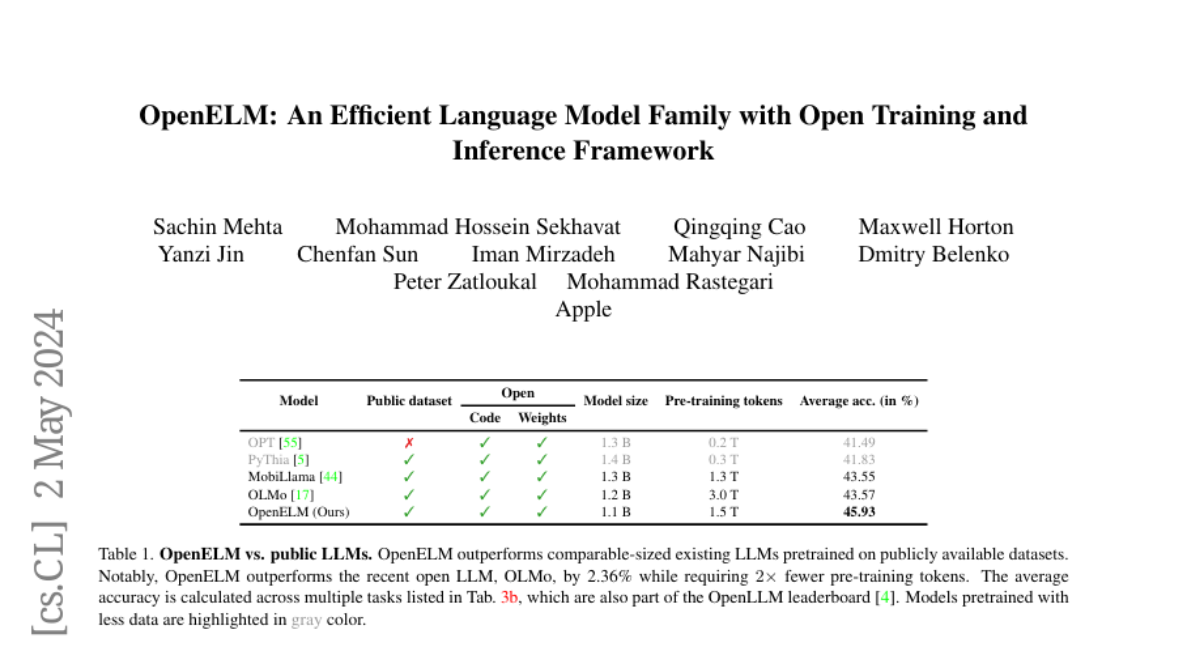
The reproducibility and transparency of large language models are crucial for advancing open research, ensuring the trustworthiness of results, and enabling investigations into data and model biases, as well as potential risks. To this end, we release OpenELM, a state-of-the-art open language model. OpenELM uses a layer-wise scaling strategy to efficiently allocate parameters within each layer of the transformer model, leading to enhanced accuracy. For example, with a parameter budget of approximately one billion parameters, OpenELM exhibits a 2.36% improvement in accuracy compared to OLMo while requiring $2\times$ fewer pre-training tokens. Diverging from prior practices that only provide model weights and inference code, and pre-train on private datasets, our release includes the complete framework for training and evaluation of the language model on publicly available datasets, including training logs, multiple checkpoints, and pre-training configurations. We also release code to convert models to MLX library for inference and fine-tuning on Apple devices. This comprehensive release aims to empower and strengthen the open research community, paving the way for future open research endeavors. Our source code along with pre-trained model weights and training recipes is available at \url{https://github.com/apple/corenet}. Additionally, \model models can be found on HuggingFace at: \url{https://huggingface.co/apple/OpenELM}.
Multi-Head Mixture-of-Experts

Sparse Mixtures of Experts (SMoE) scales model capacity without significant increases in training and inference costs, but exhibits the following two issues: (1) Low expert activation, where only a small subset of experts are activated for optimization. (2) Lacking fine-grained analytical capabilities for multiple semantic concepts within individual tokens. We propose Multi-Head Mixture-of-Experts (MH-MoE), which employs a multi-head mechanism to split each token into multiple sub-tokens. These sub-tokens are then assigned to and processed by a diverse set of experts in parallel, and seamlessly reintegrated into the original token form. The multi-head mechanism enables the model to collectively attend to information from various representation spaces within different experts, while significantly enhances expert activation, thus deepens context understanding and alleviate overfitting. Moreover, our MH-MoE is straightforward to implement and decouples from other SMoE optimization methods, making it easy to integrate with other SMoE models for enhanced performance. Extensive experimental results across three tasks: English-focused language modeling, Multi-lingual language modeling and Masked multi-modality modeling tasks, demonstrate the effectiveness of MH-MoE.
Pegasus-v1 Technical Report

This technical report introduces Pegasus-1, a multimodal language model specialized in video content understanding and interaction through natural language. Pegasus-1 is designed to address the unique challenges posed by video data, such as interpreting spatiotemporal information, to offer nuanced video content comprehension across various lengths. This technical report overviews Pegasus-1's architecture, training strategies, and its performance in benchmarks on video conversation, zero-shot video question answering, and video summarization. We also explore qualitative characteristics of Pegasus-1 , demonstrating its capabilities as well as its limitations, in order to provide readers a balanced view of its current state and its future direction.
SnapKV: LLM Knows What You are Looking for Before Generation

Large Language Models (LLMs) have made remarkable progress in processing extensive contexts, with the Key-Value (KV) cache playing a vital role in enhancing their performance. However, the growth of the KV cache in response to increasing input length poses challenges to memory and time efficiency. To address this problem, this paper introduces SnapKV, an innovative and fine-tuning-free approach that efficiently minimizes KV cache size while still delivering comparable performance in real-world applications. We discover that each attention head in the model consistently focuses on specific prompt attention features during generation. Meanwhile, this robust pattern can be obtained from an `observation' window located at the end of the prompts. Drawing on this insight, SnapKV automatically compresses KV caches by selecting clustered important KV positions for each attention head. Our approach significantly reduces the growing computational overhead and memory footprint when processing long input sequences. Specifically, SnapKV achieves a consistent decoding speed with a 3.6x increase in generation speed and an 8.2x enhancement in memory efficiency compared to baseline when processing inputs of 16K tokens. At the same time, it maintains comparable performance to baseline models across 16 long sequence datasets. Moreover, SnapKV can process up to 380K context tokens on a single A100-80GB GPU using HuggingFace implementation with minor changes, exhibiting only a negligible accuracy drop in the Needle-in-a-Haystack test. Further comprehensive studies suggest SnapKV's potential for practical applications.
FlashSpeech: Efficient Zero-Shot Speech Synthesis

Recent progress in large-scale zero-shot speech synthesis has been significantly advanced by language models and diffusion models. However, the generation process of both methods is slow and computationally intensive. Efficient speech synthesis using a lower computing budget to achieve quality on par with previous work remains a significant challenge. In this paper, we present FlashSpeech, a large-scale zero-shot speech synthesis system with approximately 5\% of the inference time compared with previous work. FlashSpeech is built on the latent consistency model and applies a novel adversarial consistency training approach that can train from scratch without the need for a pre-trained diffusion model as the teacher. Furthermore, a new prosody generator module enhances the diversity of prosody, making the rhythm of the speech sound more natural. The generation processes of FlashSpeech can be achieved efficiently with one or two sampling steps while maintaining high audio quality and high similarity to the audio prompt for zero-shot speech generation. Our experimental results demonstrate the superior performance of FlashSpeech. Notably, FlashSpeech can be about 20 times faster than other zero-shot speech synthesis systems while maintaining comparable performance in terms of voice quality and similarity. Furthermore, FlashSpeech demonstrates its versatility by efficiently performing tasks like voice conversion, speech editing, and diverse speech sampling. Audio samples can be found in https://flashspeech.github.io/.
Transformers Can Represent $n$-gram Language Models
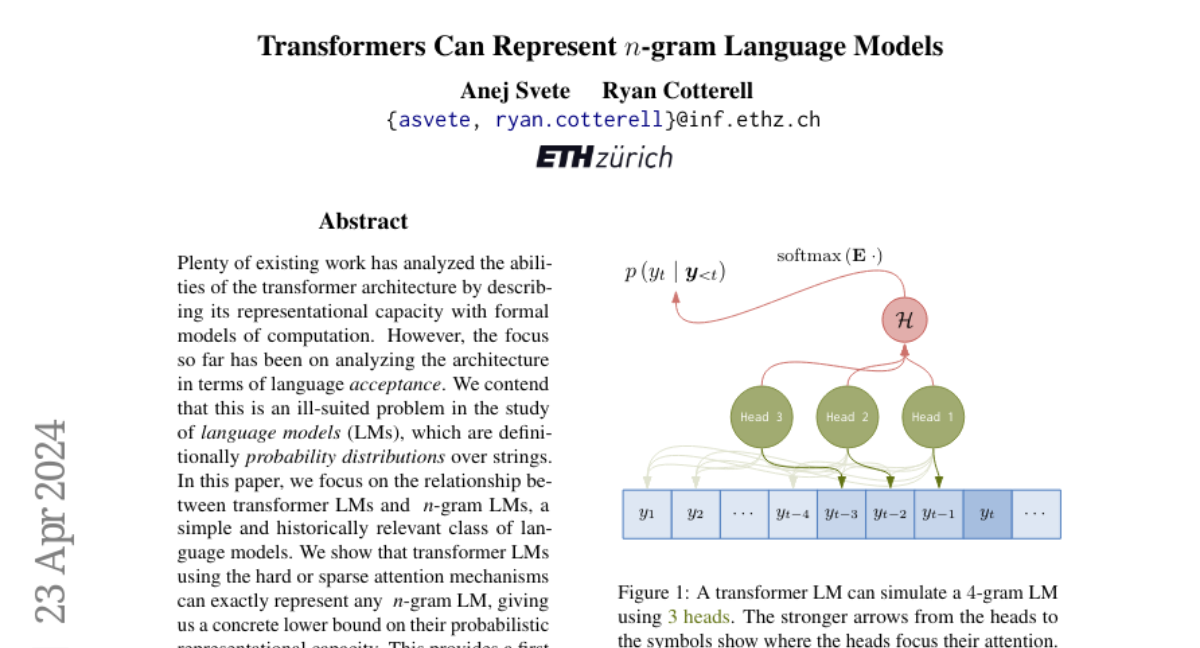
Plenty of existing work has analyzed the abilities of the transformer architecture by describing its representational capacity with formal models of computation. However, the focus so far has been on analyzing the architecture in terms of language \emph{acceptance}. We contend that this is an ill-suited problem in the study of \emph{language models} (LMs), which are definitionally \emph{probability distributions} over strings. In this paper, we focus on the relationship between transformer LMs and $n$-gram LMs, a simple and historically relevant class of language models. We show that transformer LMs using the hard or sparse attention mechanisms can exactly represent any $n$-gram LM, giving us a concrete lower bound on their probabilistic representational capacity. This provides a first step towards understanding the mechanisms that transformer LMs can use to represent probability distributions over strings.
Align Your Steps: Optimizing Sampling Schedules in Diffusion Models

Diffusion models (DMs) have established themselves as the state-of-the-art generative modeling approach in the visual domain and beyond. A crucial drawback of DMs is their slow sampling speed, relying on many sequential function evaluations through large neural networks. Sampling from DMs can be seen as solving a differential equation through a discretized set of noise levels known as the sampling schedule. While past works primarily focused on deriving efficient solvers, little attention has been given to finding optimal sampling schedules, and the entire literature relies on hand-crafted heuristics. In this work, for the first time, we propose a general and principled approach to optimizing the sampling schedules of DMs for high-quality outputs, called $\textit{Align Your Steps}$. We leverage methods from stochastic calculus and find optimal schedules specific to different solvers, trained DMs and datasets. We evaluate our novel approach on several image, video as well as 2D toy data synthesis benchmarks, using a variety of different samplers, and observe that our optimized schedules outperform previous hand-crafted schedules in almost all experiments. Our method demonstrates the untapped potential of sampling schedule optimization, especially in the few-step synthesis regime.